Navigating the realm of Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) often leads users to the renowned OpenVPN, cherished for its robust security and adaptability. However, in the quest for the most fitting VPN solution, exploring OpenVPN alternatives becomes imperative. This exploration uncovers a myriad of options, each with its own set of features, strengths, and unique attributes.
Understanding the landscape of these OpenVPN alternatives, ranging from WireGuard’s simplicity to SoftEther VPN’s versatility, is crucial in identifying the ideal match for varied user requirements. Delving deeper into the world beyond OpenVPN sheds light on the diverse spectrum of VPN solutions, empowering users to find the perfect blend of security, performance, and usability tailored to their specific needs.
Understanding OpenVPN
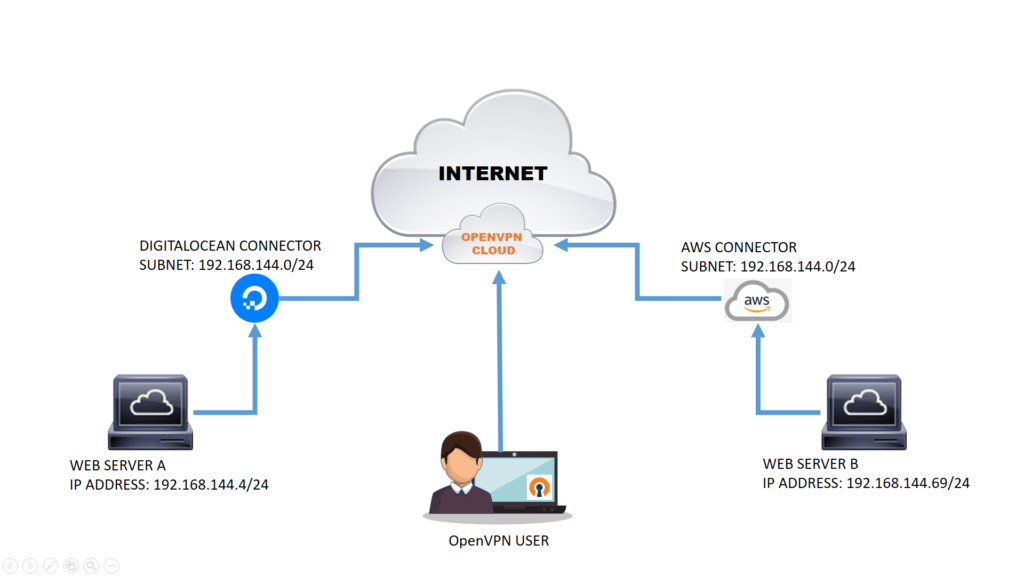
OpenVPN, a widely adopted VPN solution, boasts an open-source framework that invites continuous improvements and community-driven development. Its hallmark lies in its robust encryption protocols, cross-platform compatibility, and the ability to traverse firewalls. With configurations supporting both site-to-site and remote access, OpenVPN offers adaptability, enabling secure connections across various network architectures.
However, its setup complexity and potential speed limitations under specific conditions prompt users to explore OpenVPN alternative solutions that better align with diverse needs, seeking simpler setups, improved performance, or specialized functionalities.
Features Of OpenVPN
- Open-Source Nature: OpenVPN’s code transparency allows for community scrutiny and continual improvement.
- Strong Encryption Protocols: Utilizes robust encryption methods like OpenSSL libraries for secure data transmission.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Supports various operating systems, including Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, and Android.
- Firewall Traversal: Ability to navigate through firewalls, enabling connections in restrictive network environments.
- Site-to-Site And Remote Access Configurations: Supports both types of VPN setups, suitable for various network architectures.
- Flexibility In Protocols: Adaptable to work with different VPN protocols, including TCP, UDP, and SSL/TLS.
Limitations of OpenVPN
- Complex Configuration: Setting up and maintaining OpenVPN can be intricate and demands technical expertise.
- Potential Speed Constraints: Depending on the configuration and network conditions, speed may be affected.
- Scalability Challenges: Issues may arise when scaling OpenVPN for larger deployments.
- Dependency On Third-Party Tools: Requires external tools for user authentication and management in some instances.
What Sets OpenVPN Apart
OpenVPN stands out within the VPN landscape due to its adaptability, robust security features, and constant evolution. Unlike many other VPN solutions, OpenVPN’s open-source nature allows for continuous development and community-driven enhancements. This fosters an environment of innovation and collaboration, ensuring that security vulnerabilities are promptly addressed, and the protocol stays updated with the latest advancements in encryption and network security.
Moreover, its versatility enables it to function effectively across diverse network configurations and environments, providing a level of flexibility that accommodates various user needs. The ability to adapt to different protocols and its firewall traversal capabilities further solidify OpenVPN’s position as a reliable and secure VPN solution for both individual users and enterprises alike.
Need For OpenVPN Alternatives

The need for OpenVPN alternatives arises from varying user requirements. Some users seek simpler setups, while others prioritize speed or specific functionalities, prompting them to explore other options.
1. Diverse User Requirements
The need for alternatives to OpenVPN arises from the diverse requirements of users. While OpenVPN excels in several aspects, users often seek OpenVPN alternatives that better align with their specific needs. Some users might prioritize simplicity, seeking an alternative with an easier setup process and a more user-friendly interface.
2. Performance Optimization
In certain scenarios, users require VPN solutions that offer optimized performance, especially concerning speed and latency. OpenVPN’s performance might not always meet these specific demands, prompting users to explore OpenVPN alternatives that provide enhanced speed or better performance under certain network conditions.
3. Scalability And Business Needs
Enterprises, in particular, often face scalability challenges with OpenVPN as their network requirements grow. Consequently, the necessity to accommodate larger-scale deployments leads businesses to evaluate OpenVPN alternatives that offer seamless scalability without compromising security or efficiency.
4. Specialized Functionalities
Specific functionalities or features might be lacking in OpenVPN for some users. This could include requirements for advanced security features, specific tunneling protocols, or compatibility with particular devices or operating systems, motivating the search for alternatives catering to these specialized needs.
Commonly Used OpenVPN Alternatives For Secure Connections

Unveiling a spectrum of OpenVPN alternatives beyond OpenVPN offers users a diverse array of choices, each presenting unique strengths and functionalities. Exploring these alternatives sheds light on solutions that cater to varying preferences, from WireGuard’s efficiency to SoftEther VPN’s adaptability and beyond.
1. WireGuard
WireGuard has garnered attention for its simplistic design and exceptional performance. Its lightweight codebase contributes to faster speeds and reduced overheads without compromising security. This alternative, recognized for its modern cryptographic protocols, such as Curve25519 for key exchange and ChaCha20 for encryption, offers a streamlined setup process, making it appealing to users seeking a balance between efficiency and robust encryption. WireGuard’s novel approach focuses on simplicity and efficiency, optimizing performance across various platforms and network conditions.
2. IPsec (Internet Protocol Security)
IPsec remains a prevalent choice due to its extensive history and proven track record in providing strong security at the IP layer. It offers a suite of protocols, including AH (Authentication Header) and ESP (Encapsulating Security Payload), for secure data transmission and authentication. IPsec’s flexibility in supporting various encryption algorithms like AES and DES, along with its ability to integrate seamlessly with existing network infrastructures, makes it a reliable and standardized OpenVPN alternative across different platforms.
3. SoftEther VPN
SoftEther VPN’s open-source nature provides users with a versatile solution supporting multiple VPN protocols. Its standout feature lies in its capability to facilitate Layer 2 Ethernet bridging, allowing the creation of virtual private networks across geographically dispersed locations. The diverse protocol support, including SSL-VPN, L2TP/IPsec, and OpenVPN, grants users the flexibility to configure VPN connections based on their specific requirements. SoftEther VPN’s extensive compatibility with Windows, macOS, Linux, and other operating systems makes it an attractive choice for users seeking a comprehensive and adaptable VPN solution.
4. StrongSwan
Primarily designed for Linux environments, StrongSwan stands out with its robust IPsec-based VPN solutions. It offers a wide array of features, including IKEv2 (Internet Key Exchange version 2) support and MOBIKE (Mobility and Multihoming Protocol for IPsec) capabilities, enhancing seamless connectivity and mobility for users. StrongSwan’s scalability and compatibility with various systems, coupled with its support for different encryption protocols like AES and RSA, position it as a preferred choice for larger-scale deployments seeking enterprise-level security and performance.
5. Tinc
Tinc operates as a self-healing mesh VPN daemon, emphasizing security, ease of configuration, and reliability across multiple platforms. Its decentralized nature and ability to create dynamic VPN networks without the need for a central server make it an intriguing choice for users looking beyond traditional VPN setups. Tinc’s emphasis on peer-to-peer communication and its encryption mechanisms ensure secure data transmission among nodes, offering a high level of privacy and resilience against network disruptions.
6. Pritunl
Built upon the foundation of OpenVPN, Pritunl serves as an enterprise-grade VPN server. Its scalable architecture and intuitive user interface cater to businesses seeking manageable yet secure VPN solutions with extended administrative controls. Pritunl’s centralized management console streamlines user access and permission settings, offering businesses enhanced control over their VPN infrastructure. The compatibility with various authentication methods, including LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) and Google Authenticator, further bolsters its appeal as an enterprise-ready VPN solution.
7. ZeroTier
ZeroTier’s innovative approach to creating virtual Ethernet networks aligns with the needs of users seeking simplicity and decentralization. Its user-friendly interface and focus on ease of setup make it an appealing OpenVPN alternative for various network configurations. ZeroTier’s zero-trust model, where devices are granted access based on explicit authorization, enhances security within the network. Its ability to establish secure connections across disparate devices without complex configurations makes it suitable for scenarios requiring quick and seamless network integration.
8. OpenConnect
OpenConnect, an open-source SSL VPN client, extends support beyond Cisco’s AnyConnect SSL VPN. Its versatility in supporting different systems and diverse options for VPN configurations make it a viable choice for users seeking broader compatibility. OpenConnect’s emphasis on security and its ability to operate over both TCP and UDP protocols ensure reliable and encrypted connections across various network environments. Additionally, its open-source nature allows for community-driven improvements and updates, ensuring a continuously evolving VPN solution.
9. Shadowsocks
Primarily used to bypass internet censorship, Shadowsocks operates as a proxy, encrypting traffic to provide users with a level of anonymity. Its unique functionality caters to specific user needs, especially in regions with restricted internet access. Shadowsocks’ focus on obfuscation techniques and its ability to disguise network traffic allows users to access restricted content while maintaining a certain level of privacy. Its lightweight and versatile nature makes it an intriguing option for users seeking anonymity and circumventing online restrictions.
Factors To Consider While Choosing The Perfect “OpenVPN Alternative”

Selecting the ideal VPN alternative involves meticulous consideration of factors such as security, ease of use, compatibility, performance, and scalability. Each criterion plays a crucial role in determining the most suitable solution tailored to meet specific user requirements and preferences.
1. Security And Encryption
When selecting an OpenVPN alternative, prioritizing robust security measures is paramount. Look for VPN solutions that employ the latest encryption protocols and authentication methods. Ensuring the protection of sensitive data and maintaining user privacy should be at the forefront of the decision-making process. Features like AES encryption, RSA keys, and Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS) contribute significantly to the overall security of the VPN.
2. Ease Of Use And Configuration
User-friendliness and ease of configuration play a crucial role, especially for individuals or businesses with limited technical expertise. Consider VPN alternatives that offer intuitive interfaces, straightforward setup processes, and comprehensive documentation. Simplified management consoles and step-by-step guides can significantly enhance the user experience, making the transition from OpenVPN smoother.
3. Compatibility And Cross-Platform Support
An ideal OpenVPN alternative should seamlessly integrate across various operating systems and devices. Look for VPN solutions that offer broad compatibility, supporting Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, Android, and other platforms. Compatibility ensures flexibility in deployment and usage, allowing users to access the VPN from their preferred devices without limitations.
4. Speed And Performance
Assessing the performance metrics of alternative VPN solutions is crucial, especially if high-speed connections or low latency are essential. Conduct speed tests and evaluate latency rates to determine how well the VPN performs under different network conditions. Consider factors such as server locations, network load, and bandwidth capabilities to ensure the chosen OpenVPN alternative meets performance requirements.
5. Scalability And Business Requirements
For businesses or organizations, scalability is a key consideration when selecting an OpenVPN alternative. Ensure that the chosen VPN solution can accommodate the organization’s growth without compromising performance or security. Assess whether the alternative aligns with specific business needs, such as support for multiple users, centralized management, and compliance with industry standards.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the quest for the perfect VPN solution beyond OpenVPN reveals a diverse landscape of alternatives, each offering distinct features and catering to specific user needs. From WireGuard’s simplicity and efficiency to SoftEther VPN’s versatility and StrongSwan’s enterprise-grade security, the choices are abundant. Factors such as security, ease of use, compatibility, performance, and scalability play pivotal roles in determining the ideal OpenVPN alternative.
While OpenVPN stands as a robust and widely used option, exploring these alternatives widens the spectrum, empowering users to find the perfect fit for their unique requirements. Ultimately, the pursuit of the ideal “OpenVPN alternative” unveils a rich array of choices, ensuring users can align their VPN solution precisely with their preferences and necessities.









