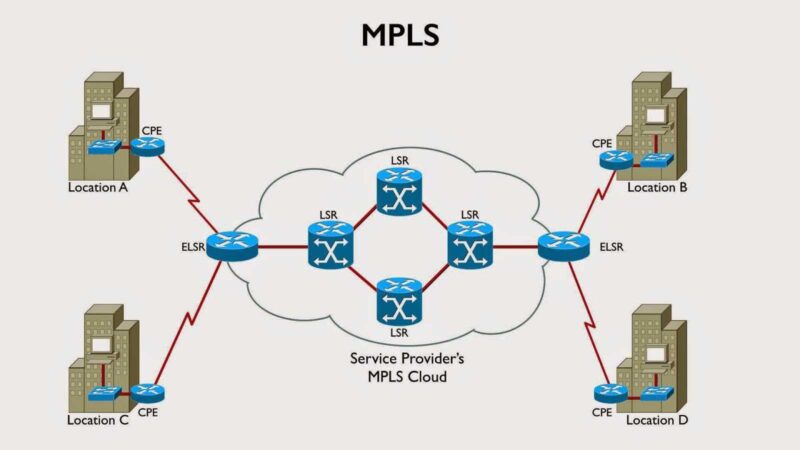
In the rapidly evolving landscape of networking technologies, finding the right solution to meet your organization’s needs is crucial. Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) has long been a staple in the networking world, offering benefits like efficient data packet forwarding and reliable service delivery. However, as the demands of modern networks continue to expand, exploring alternatives to MPLS has become an imperative. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the world of MPLS alternatives, uncovering their unique features, advantages, and how they stack up against the tried-and-true MPLS.
Features and Limitations of MPLS
Before we embark on the journey of discovering alternatives, let’s first understand what MPLS brings to the table and where it falls short. MPLS boasts features such as fast data transmission, Quality of Service (QoS) prioritization, and efficient utilization of network resources. Its label-switching mechanism allows for streamlined routing and reduced congestion.
However, MPLS has its limitations. It can be complex to set up and manage, often requiring specialized knowledge. Scalability can also be a concern, particularly as network demands surge. As businesses increasingly rely on cloud services and demand real-time data delivery, these limitations become more pronounced.
What Sets MPLS Alternatives Apart
MPLS alternatives bring a fresh perspective to networking, offering a range of capabilities that cater to modern demands. From embracing software-defined principles to enhancing security, these alternatives provide a holistic approach to networking. Let’s dive into the realm of MPLS alternatives and explore the unique strengths they bring to the forefront.
The Need for MPLS Alternatives
As technology evolves and business needs shift, the need for viable alternatives to MPLS becomes more pronounced. This need arises due to several critical factors that shape the modern networking landscape:
1. Agility and Adaptability
Modern businesses require networks that can swiftly adapt to changing demands. The static nature of MPLS can hinder rapid changes to network configurations, making it less suitable for dynamic environments. Alternatives such as SD-WAN excel in this regard, dynamically optimizing traffic flow based on real-time conditions.
2. Cloud-Centric Operations
The rise of cloud computing has transformed the way data is stored and accessed. MPLS, originally designed for traditional network architectures, may not seamlessly integrate with cloud services, necessitating alternatives that can provide better cloud connectivity and performance. SD-WAN, for instance, optimizes cloud application performance by intelligently selecting the optimal path for traffic.
3. Global Connectivity and Remote Workforces
In an era of global connectivity and remote workforces, networks must cater to diverse geographical locations. MPLS’s reliance on physical infrastructure may not efficiently support the seamless connection of widely dispersed sites. Solutions like DMVPN address this challenge by creating secure and efficient VPN connections across geographically distributed locations.
4. Bandwidth Intensive Applications
The proliferation of bandwidth-intensive applications, such as video conferencing and data streaming, demands networks that can handle high data volumes without compromising performance. MPLS’s limitations in scalability could pose challenges in supporting such applications effectively. VXLAN, on the other hand, enhances network scalability and is well-suited for data center environments hosting these applications.
Commonly Used MPLS Alternatives For Next-Gen Networking

1. Segment Routing (SR)
Segment Routing emerges as a game-changer, allowing network architects to dictate precise paths for data packets. This dynamic approach eliminates the need for complex protocols by using a label stack to define segments. SR not only enhances network flexibility but also offers robust traffic engineering capabilities.
2. SD-WAN (Software-Defined Wide Area Network)
SD-WAN takes center stage in the era of distributed workforces and cloud-centric operations. By intelligently routing traffic across diverse network paths, SD-WAN optimizes performance and resilience. It embraces multiple transport technologies, from MPLS to broadband, adapting to changing network conditions in real time.
3. VXLAN (Virtual Extensible LAN)
VXLAN revolutionizes network virtualization in data centers. With the ability to create virtual Layer 2 networks over existing Layer 3 infrastructure, VXLAN ensures isolation, scalability, and simplified management of network segments.
4. IPsec (Internet Protocol Security)
For organizations prioritizing secure communication and VPN deployment, IPsec remains a stalwart. By encrypting data and establishing secure tunnels, IPsec safeguards sensitive information from prying eyes and unauthorized access.
5. BGP/MPLS VPNs
Leveraging the power of BGP, this alternative builds virtual private networks over service provider networks. Its scalability and flexibility make it an attractive option for businesses seeking efficient interconnection of geographically dispersed sites.
6. DMVPN (Dynamic Multipoint Virtual Private Network)
DMVPN shines in the realm of scalable and secure VPNs. Its hub-and-spoke architecture simplifies network setup while ensuring data privacy and reliable connectivity for remote locations.
7. P4 (Programming Protocol-Independent Packet Processors)
P4 empowers network administrators to customize packet processing, tailoring network behavior to specific requirements. This programmable approach enhances adaptability and responsiveness in dynamic environments.
8. NVGRE (Network Virtualization using Generic Routing Encapsulation)
NVGRE, similar to VXLAN, enables the creation of isolated Layer 2 networks over IP infrastructure. It finds relevance in scenarios where network virtualization is critical, such as cloud deployments.
9. OpenFlow
As a cornerstone of software-defined networking, OpenFlow enables centralized control over network flows. It ushers in a new era of network management, promoting agility and efficient resource utilization.
Factors To Consider While Choosing The Perfect MPLS Alternative

Selecting the ideal MPLS alternative necessitates careful consideration of various factors. As you embark on this transformative journey, keep the following aspects in mind:
1. Scalability
Evaluate whether the alternative can seamlessly accommodate your organization’s growth trajectory. Scalability ensures that your network solution remains viable as demands escalate. Solutions like Segment Routing and SD-WAN offer scalable architectures that can evolve with your network’s needs.
2. Flexibility and Customization
Look for solutions that allow you to tailor network behavior to suit specific applications and services. The ability to adapt quickly to changing requirements is invaluable. P4, for instance, enables granular customization of packet processing to optimize network performance.
3. Security
Security is paramount in the digital age. Ensure that the chosen alternative provides robust encryption, authentication, and protection against emerging threats. IPsec stands as a robust choice for securing data transmissions and maintaining the integrity of communications.
4. Cost-Effectiveness
Consider the overall cost of implementation, maintenance, and operation. An alternative that offers a balance between features and cost can yield long-term benefits. SD-WAN’s cost-effective utilization of diverse network paths can lead to significant savings over traditional MPLS solutions.
5. Integration with Existing Infrastructure
Smooth integration with your current network setup is essential. The transition should be seamless, minimizing disruption to ongoing operations. BGP/MPLS VPNs, designed for interoperability, can ease the migration process by working harmoniously with your existing network architecture.
Conclusion
In the realm of networking, the pursuit of alternatives to MPLS is fueled by the need for innovation and adaptability. As technology continues to advance, businesses can leverage a diverse array of options to create agile, secure, and high-performing networks. From Segment Routing’s dynamic path control to SD-WAN’s intelligent traffic management, the landscape of MPLS alternatives is brimming with solutions that cater to the demands of the digital era. By carefully evaluating the unique strengths of each alternative and aligning them with your organization’s goals, you can pave the way for a network infrastructure that is primed for success in the ever-evolving digital landscape.