Have you ever attempted to store a file on a removable media device, such as a USB drive or an SD card, only to find that the device lacked sufficient space? Even if you are certain you have the necessary permissions to move the files, there are instances in which you will be unable to do so.
Why Do You Get an Error Saying Your File Is Too Big?
The Windows File System is indispensable for comprehending this error. A computer’s file system is the framework or system by which Windows classifies and organizes files of different types and extensions.
This term is also applicable to the various sections of a hard drive. An error message reading the file is too large for the destination file system indicates that the files you attempted to upload were too large to fit on the specified drives. Repetition will not solve this problem.
Understanding the different device formats is a precondition for identifying a viable solution to this issue. The four system file formats backed by Windows are ExFAT, FAT, FAT32, and NTFS.
4 Windows File System Formats
1. The FAT Format or File Allocation Table
The FAT format is the most fundamental component of Windows’ file management system. It does not have the same level of efficiency as more recent versions of the file system. In the FAT file format, you can only upload files that are less than 2 gigabytes in size.
2. The FAT32 Format
Because it’s compatible with various operating systems, FAT32 is the file system of choice for a hard drive with a limited storage capacity. The maximum file size that can be saved using the FAT32 file system is 4 gigabytes.
3. ExFat is also known as FAT64
It wasn’t too long ago that people weren’t using file formats like exFAT or FAT64. Even though it can be used with various storage media, the best results are achieved using flash memory. The only significant drawback it has is that this file system is not compatible with other operating systems.
4. The NTFS Format or New Technology File System
As a result of its compatibility with a wide range of operating systems, NTFS has emerged as the industry standard for file storage. This technique works well with hard drives with enormous storage capacities, such as 16 terabytes.
What to Do if the File is Too Large for the Destination?
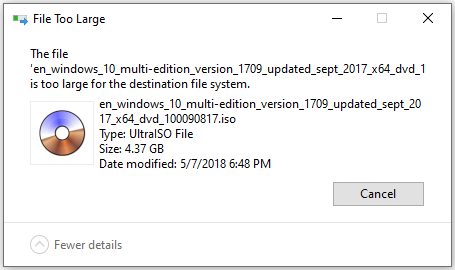
If the file is too large for the location system files error message appears in Windows 10, here’s what to do. Before changing things to the file system configuration, you should back up your files to another storage device.
Formatting the drive in NTFS instead of FAT32
It’s well known that the maximum file size that can be transferred or obtained using FAT32 is 4 GB. One can install a newer file system like NTFS or exFAT on this. As a result, the larger file size can be increased from 4 gigabytes of storage to 16 terabytes, much larger than most existing storage capacities.
Follow these steps to change the format:
- To open the Command Prompt, either type cmd into the search bar or press the Windows key in combination with the R key to open the run dialog.
- To execute, type the following command into the script window and press the Enter key: convert “ FAT32 partition drive letter”: /fs:ntfs
- You may also be required to enter the process’s volume label to finish this operation. Then attempt a file transfer. If the data is transferred, you successfully migrate from FAT32 to NTFS.
The storage unit should be formatted.
It’s not recommended to format the device because you may lose all of its data. This, however, will convert the Windows operating system to a format of your selection, potentially resolving the location file system issue.
Here are the steps to format your storage unit and change the file system:
- After connecting the USB device, start up This PC on your computer.
- You can format the USB storage device by right-clicking its partition and selecting “Format.” The “Device Format” dialogue box will appear.
- In the File system drop-down arrow, select NTFS or exFAT.
- You can start the process by selecting the Start button.
This process may take a few seconds, depending on the device’s capabilities. Nevertheless, all data stored on the removable media will be erased. Make backups if you need the files on the storage device.
Conclusion
These are a few suggestions for resolving the error if the transferred file is too large for the designated location. However, always keep a backup of important data before performing any of these processes.









